66) What are acids and alkalis sources of?
Answer 66Acids – hydrogen ions (H+)
Alkalis – hydroxide ions (OH–)
67) What are the colour changes of?
- Litmus
- Methyl orange
- Phenolphthalein
With acid and alkali?
Answer 67| Acid | Alkali | |
| Litmus | red | blue |
| Methyl orange | red | yellow |
| Phenolphthalein | colourless | pink |
68) What is the link between hydrogen ion concentration and pH?
Answer 6869) When calcium hydroxide is added slowly to hydrochloric acid the pH of the resulting solution changes. What would the graph of this look like?
Answer 69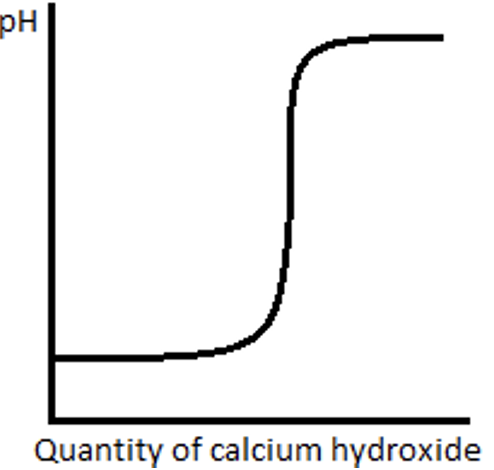
70) What pH could a concentrated acid have?
Answer 7071) Which would have a pH of 1?
- 1 mol dm-3 Sulphuric acid (a strong acid)
- 10 mol dm-3 Ethanoic acid (a weak acid)
72) What is a base?
Answer 7273) What is an alkali?
Answer 7374) What type of reaction is it when an acid reacts with a base?
Answer 7475) What are the products of the following neutralisation reactions?
- Metal + acid =
- Metal oxide + acid =
- Metal hydroxide + acid =
- Metal carbonate + acid =
- Salt + hydrogen
- Salt + water
- Salt + water
- Salt + water + carbon dioxide
76) What is the chemical test for?
- Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide
- Lit splint gives a squeaky pop.
- Bubbling carbon dioxide through limewater turns it milky.
77) Explain why water is produced when an acid reacts with an alkali?
Answer 7778)When preparing a soluble salt from an acid an insoluble reactant how do you ensure the salt is pure?
Answer 33- Use excess insoluble reactant to neutralise all the acid.
- Filter the resulting mixture to remove the excess reactant.
79) How do you prepare a soluble salt when both the reactants are soluble?
Answer 7980) How would you prepare a sample of pure, dry hydrated copper sulfate crystals starting from copper oxide.
Answer 80- Add excess copper oxide to sulfuric acid and place in a water bath to gently heat.
- Filter the mixture to remove excess copper oxide.
- Evaporate the mixture, this can be heated to start with but it must be left to evaporate at room temperature to produce hydrated crystals.
81) How do you carry out an acid-alkali titration, using burette, pipette and a suitable indicator, to prepare a pure, dry sample of sodium chloride?
Answer 81- Fill a burette with hydrochloric acid.
- Measure 25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide using a pipette and place in a conical flask.
- Add a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
- Place the conical flask on a white tile underneath the burette.
- Run in hydrochloric acid fairly quickly at first whilst continually stirring.
- When the neutralisation point is approaching start to add the acid drop wise.
- Stop adding the acid the moment the indicator goes clear.
- Repeat the titration 2 further times and average results.
- Carry out titration one final time, this time without indicator to ensure the salt produced is pure. Stop adding acid when the average quantity previously identified has been added.
82) Are the common sodium, potassium and ammonium salts soluble or insoluble?
Answer 8283) Are nitrates soluble or insoluble?
Answer 8384) Are common chlorides soluble or insoluble? And what is the exception to the rule?
Answer 8485) Are common sulfates soluble or insoluble? And what is the exception to the rule?
Answer 8586) Are common carbonates and hydroxides soluble or insoluble? And what is the exception to the rule?
Answer 8687) What is a precipitate?
Answer 8788) What is the name of the insoluble precipitate formed when lead nitrate reacts with potassium chloride?
Answer 8889)How do you prepare a pure, dry sample of an insoluble salt?
Answer 89