20) How could you monitor the rate of a reaction?
Answer 20 By looking at how quickly a product like a gas is produced, this could be done by collecting the gas in a syringe. Alternatively, by seeing how quickly a reactant is used up, this could be done by monitoring the mass of solid reactant.
21) If a reaction is to occur what 2 things need to happen between reacting particles?
Answer 21 The particles must collide and the collision must have enough energy.
22) Explain why increasing the temperature speeds up a reaction.
Answer 22 It gives the particles more energy so they collide more often and the collisions have more energy.
23) Explain why increasing the concentration of a solution speeds up a reaction.
Answer 23 It means there are more particles present so it will increase the number of collisions.
24) Explain why increasing the pressure on reactions involving gases speeds up the rate of reaction.
Answer 24 Increasing the pressure increases the number of gas particles present in a certain volume. This increases the number collisions between reacting particles, which increases the rate of reaction.
25) Explain how breaking up a solid reactant increases the rate of reaction.
Answer 25 Breaking up a solid increases the surface area. This means that there is a greater area of solid exposed for other particles to collide with. This increases the likelihood of a successful collision and therefore speeds up the reaction.
26) What happens to the rate as a reaction progresses and what would a rate of reaction graph look like?
Answer 26 Reactions start quickly and slow down as they progress. A rate curve will start off steep and the gradient will continually decrease to reflect the changing rate.
27) What is a catalyst?
Answer 27 A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction without altering the products of the reaction, being itself unchanged chemically and in mass at the end of the reaction.
28) How does a catalyst speed up a reaction?
Answer 28 A catalyst provides an alternative route which requires less activation energy.
29) What are enzymes and what are they used for?
Answer 29 Enzymes are biological catalysts and they are used in the production of alcoholic drinks.
30) What is an exothermic reaction and give an example?
Answer 30 A reaction that gives out heat energy. For example combustion.
31) What is an endothermic reaction and give an example?
Answer 31 A reaction that takes in heat energy. For example photosynthesis.
32) Is the breaking of bonds exothermic or endothermic?
Answer 32 Endothermic.
33) Is the making of bonds exothermic or endothermic?
Answer 33 Exothermic.
34) Why is a reaction exothermic?
Answer 34 In an exothermic reaction less heat energy is needed to break bonds than is given out when new bonds are made.
35) Why is a reaction endothermic?
Answer 35 In an endothermic reaction less energy is released in forming bonds in the products than is required in breaking bonds in the reactants.
36) How do you calculate the energy change in a reaction?
Answer 36
Bond breaking – bond making.
The energy required to break bonds – energy given out when bonds are formed.If the answer is negative then the reaction is giving out energy and is exothermic.
37) What is the unit for measuring the energy change in reactions?
Answer 37 KJ mol-1 (kilojoule per mole)
38) What is meant by the term activation energy?
Answer 38 The energy needed for a reaction to start. This is equal to the energy needed to break all the reactants’ bonds.
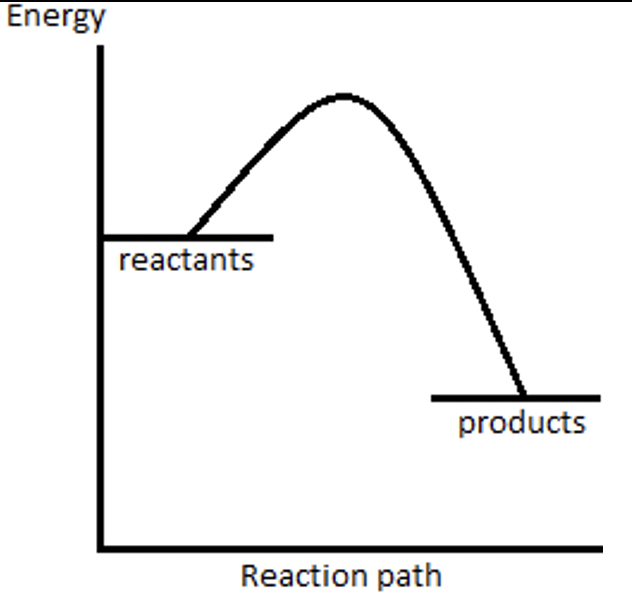
39) What does the reaction profile for an exothermic reaction look like?
Answer 39
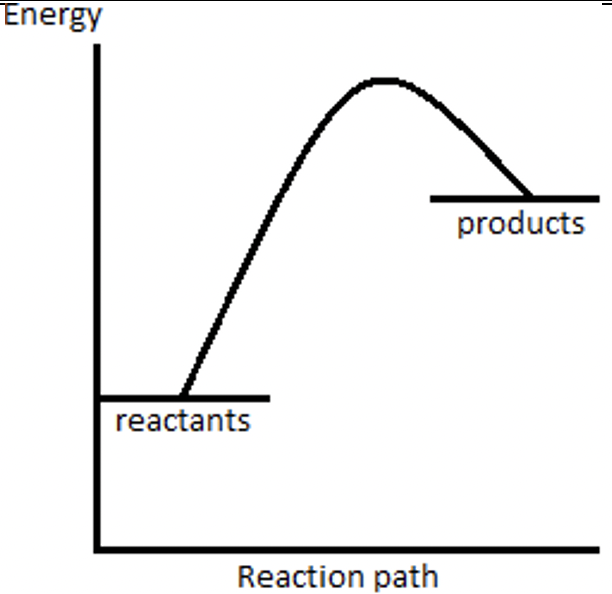
40) What does the reaction profile for an endothermic reaction look like?
Answer 40