41) What is a hydrocarbon?
Answer 4142) What is crude oil?
Answer 4243) With respect to crude oil, what is a “fraction”?
Answer 4344) What is the name of the process used to separate crude oil into its fractions?
Answer 4445) How does the fractional distillation of crude oil work?
Answer 4546) The fractions come off the fractionating column in the following order (starting from the top of the column). Name the uses of each fraction:
- Refinery gases
- Petrol
- Kerosene
- Diesel oil
- Fuel oil
- Bitumen
- domestic heating and cooking
- fuel for cars
- fuel for aircraft
- fuel for some cars and trains
- fuel for large ships and in some power stations
- used to surface roads and roofs
47) Hydrocarbons in different fractions differ from each other in:
Number of carbon atoms in their molecules, boiling points, ease of ignition (flammability) and viscosity (stickiness).
a) which fraction has the most carbon atoms in its molecules (the longest carbon chain)?
b) which fraction has the lowest boiling point?
c) which fraction is the hardest to ignite (least flammable)?
d) which fraction has the lowest viscosity?
Answer 47a) bitumen
b) refinery gases
c) bitumen
d) refinery gases
48) What is a homologous series?
Answer 4849) What are the reactants and products of the complete combustion of hydrocarbons?
Answer 49Products – carbon dioxide and water ONLY.
(Energy is released, but it is not a product, because it is not a chemical substance.)
50) What are the products of the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons? Why are they different from the products of complete combustion?
Answer 50Carbon monoxide (CO) and/or carbon (C) are produced because there is not enough oxygen available to form carbon dioxide (CO2).
51) Why are we concerned about incomplete combustion?
Answer 5152) What effect does carbon monoxide have on the body?
Answer 5253) What is “acid rain”, and how does it arise?
Answer 5354) What are the problems associated with acid rain?
Answer 54Acid rain damages the leaves and roots of plants and trees.Acid rain can speed up the weathering of limestone (rocks or buildings) and marble.
55) How are nitrogen oxides produced?
Answer 5556) What is a nonrenewable fuel?
Answer 5657) What is the cause of a sooty flame?
Answer 5758) Give an advantage and a disadvantage of combining hydrogen and oxygen in a fuel cell¸ rather than petrol, as a fuel for cars.
Answer 58Disadvantage – hydrogen can be explosive/hydrogen is not readily available in filling stations at present /the process needed to produce the hydrogen fuel results in the production of carbon dioxide.
59) Are alkanes saturated or unsaturated?
Answer 5960) What is the formula for:
- methane
- ethane
- propane
Draw the structures of these molecules.
Answer 60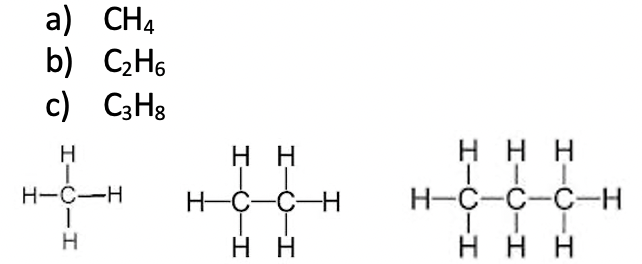
61) What is the formula for the alkenes:
- ethene
- propene
- C2H4
- C3H6
62) a) Explain what “cracking” is, and what products are made.
b) Why do oil companies bother to carry out this reaction?
Answer 62a) Cracking is the splitting (using heat) of a long chain saturated hydrocarbon (an alkane) to form a shorter chained alkane and an alkene.
b) Shorter chained hydrocarbons make better fuels. Crude oil contains too many of the longer chained molecules, so oil companies crack them to i) make more of the useful fuels, and ii) make alkenes (which can be used to make polymers).
63) How was the earth’s first atmosphere formed?
Answer 6364) What are thought to be the relative proportions of the gases that formed the early atmosphere?
Answer 6465)Why can’t we be certain about how the earth’s atmosphere formed?
Answer 6566) How were the earth’s oceans formed?
Answer 6667) How did the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere gradually increase?
Answer 6768) What is a chemical test for oxygen?
Answer 6869) Describe the processes, other than photosynthesis, that reduced the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Answer 69- Carbon dioxide dissolved into the oceans.
- Dissolved carbon dioxide was incorporated into the shells of marine organisms. When marine organisms die their shells can eventually form carbonate rocks.
70) What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer 7071) What evidence do we have for global warming and why can we not be absolutely certain about it?
Answer 71Scientists have discovered a correlation between historical global temperature and carbon dioxide levels. They also know how much carbon dioxide we are presently adding to the atmosphere.
We cannot be certain about this because of historical accuracy of the temperature and carbon dioxide levels and also due to uncertainties caused by the location where measurements are taken.
72) List the percentages of the gases in our modern atmosphere.
Answer 7273) What are the potential effects on the climate of increased levels of carbon dioxide and methane caused by human activity?
Answer 7374) How might the greenhouse effect be mitigated?
Answer 7475) Why can we not just stop burning fossil fuels to generate electricity?
Answer 75